Rizal Philippines
August 31, 2015
From Medical Health Guide - Health Benefits of Makabuhay
Health Benefits of Makabuhay from Stuart Exchange
Scientific Name: Tinospora cordifolia
Also knows as:
Makabuhay (Tagalog), Heavenly elixir (English), Guduchi, Gulancha Tinospora (India)
Makabuhay (Tagalog), Heavenly elixir (English), Guduchi, Gulancha Tinospora (India)
There is a makabuhay plant growing in front of our house. I understand this has medicinal use, and there are plenty of health benefits.
It has been known to be used for abortion (contrary to its) name, But its main benefits include:
1. anti malaria
2. anti cancer
3. for treatment of HIV
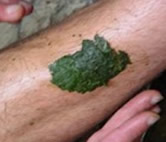
4. as poultice for treatment of wounds, scabies and other flesh wounds.
5. anti fever
6. diabetes
7. vs. gout and arthritis
8. malaria,
9. impotence
10. hepatitis
11. anemia
- Makabuhay roots, stems and leaves are used as herbal treatment for fevers, Malaria. Makabuhay leaves and roots are pounded then dissolved in cold water. Applied with a soft cloth over the nape, forehead, underarms and other body parts to bring down the body temperature.
- Most of the medicinal uses and health benefits of Makabuhay listed are based on traditional beliefs and practices.
- Makabuhay poultice is used to treat gout, arthritis, and rheumatism by reducing pain and edema.
- Makabuhay is used to treat skin diseases (athlete’s foot, scabies, etc.), promotes wound healing and alleviate skin itching.
 Makabuhay tonic is believed to promote overall good health and longevity, improves memory, improves skin tone and texture, and provides energy.
Makabuhay tonic is believed to promote overall good health and longevity, improves memory, improves skin tone and texture, and provides energy.- Makabuhay tonic is also used to treat fever and malaria.
- Makabuhay tonic is used to treat gastrointestinal and digestive problems, which includes diarrhea, hyperacidity, abdominal pains, gas pains (kabag), vomiting, dyspepsia, dysentery, colitis, constipation, loss of appetite and even worm infestation.
- Makabuhay is also used in the treatment of diabetes, heart problems, hepatitis, anemia, impotence, tuberculosis, jaundice,
Makabuhay, Herbal Medicine Preparation



Makabuhay tea or tonic preparation:
- gather fresh Makabuhay leaves and stems,
- cut in small pieces
- wash with fresh water
- boil 50 grams of Makabuhay leaves to a liter of water
- let it seep for 10 minutes
- remove from heat
- Strain
- drink while warm up to 2 cups a day.
- gather fresh leaves, stems and roots
- wash with fresh clean water
- pound in a mortar
- grounded leaves and stems may be applied or a juice extract may be used
- other herbs and coconut oil may also be mixed.
- Applied directly onto the affected area.
A spoonful of dried leaves and thinly chopped stems are boiled in a cup of water. Drink one cup per day.
Makabuhay, Scientific Studies - Medical Uses
Diabetes and Tinospora Cordifolia
 Studies
Studies
• Hay Fever / Allergic Rhinitis: A study in the Indira Ghandi Medical College showed it effective in relieving symptoms of hay fever or allergic rhinitis. The study used the supplement Tinofend 300 mg three times a day.
• Anti-scabies: Tinospora rumphii Boerl. (Makabuhay) in the Treatment of Scabies: The study established the acaricidal property of Tinospora rumphii. A concomitant antimicrobial action could not be ruled out.
• Furanoid Diterpenes: Study yielded cleordane type furanoid diterpenes: a new rumphioside I and known borapetodies C and F, plus three other compounds. (6)
• Clerodane Diterpenes: Study yielded two new diterpenes, 1 and 2, from the leaves of Tinospora rumphii, along with known compounds tinotufolin D and vitexilactone. (7)
• Swine Diarrhea Control: Study showed reduction of diarrhea with use of 25% fresh makabuhay decoction from day 15-35 in piglets with diarrhea. (8)
• Antifertility Effect: Study on Sprague-Dawley rats investigated the effect of T rumphii on the activity of 3-B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in the ovary. (9)
• Hypoglycemic / Hypolipidemic: Study on the extract of Tinospora cordifolia roots for 6 weeks resulted in a significant reduction of blood and urine glucose and lipids in serum and tissues in alloxan diabetic rats.
(10)
• Antimicrobial / Diterpenes: Study on chloroform extract of air-dried leaves yielded a new clerodane diterpene, B2, and known diterpenes B1, tinotufolin D (B5) and vitexilactone (B3). B2 was found to have antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger and T. mentagrophytes, and antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis. (11)
• Hypoglycemic / Insulinotropic Activity: Study of aqueous extract on alloxan-diabetic rats showed significant reduction of blood glucose and higher levels of serum insulin levels. The insulinotropic effect was also evident in perifused human and rat islets and HIT-T5 B cells. Results suggest the hypoglycemic effect is associated with increased insulin secretion. (14)
• No Diabetic Benefits / Human Study: Study of dry powder capsule of Tinospora crispa in healthy and type 2 diabetic patients showed no effect on serum glucose and insulin levels. The result was inconsistent with other studies in animal model and metabolic syndrome subjects. (15)
• Anti-TNF-a / Prevention of Atherosclerosis-related Cardiovascular Diseases: Study investigated an aqueous and methanol extract on Tumor Necrosis Factor induced inflammation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial cells in vitro. Results showed T. crispa extracts have an inhibitory effect in vitro on the levels of inflammation signaling molecules and may have potential in the development of nutraceuticals for the prevention of atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular diseases. (16)
• Toxicity Study / Prolonged Use Concern: Results of chronic toxicity study of ethanolic extract suggest that, due to observed hepatic and renal toxicity potential in rats, prolonged use of high doses of T. crispa in humans should be avoided or discontinued immediately if signs of liver or renal toxicities occur while using T. crispa. (17)
• Antimicrobial / Cytotoxicity / Antioxidant: Various extracts showed very significant cytotoxicity on brine shrimp lethality bioassay. Strong antioxidant activity was seen on DPPH assay. A chloroform soluble fraction of the methanolic extract showed significant activity against tested organisms on antimicrobial screening. (18)
• Borapetoside C / Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Study isolated the hypoglycemic actions of borapetoside C isolated from T. crispa. Results showed borapetoside C can increase glucose utilization, delay the development of insulin resistance and enhance insulin sensitivity. (19)
• Antioxidative / Antiatheroslcerosis: Study investigated the effect of T. crispa stem aqueous extract in hypercholesterolemic-induced rabbits. Results showed improvement in lipid profile (decreased total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, and increased HDL). Extract also showed strong antioxidative properties and markedly reduced atheroslcerotic lesion formation. Results suggest a potential for incorporation of T. crispa as part of therapeutic regimens in the prevention of atherosclerosis. (20)
• Hepatotoxin Concerns: Study evaluated the effect of an ethanolic extract of dried stems of T. crispa i a male rat model of hepatic fibrosis caused by the hepatotoxin, thioacetamide. Results showed a significant increase in the activity of liver enzymes. The in vivo study establishes the extract contains hepatotoxins and suggests reliance on data from in vitro methodologies may lead to erroneous conclusions. (21)
• Antioxidative / Antiproliferative: Study evaluated the cytotoxicity potential and antioxidant activity of various extracts. A methanol extract showed the highest flavonoid and phenolic content, with highest scavenging activity in a dose-dependent manner. T. crispa also showed dose-dependent antiproliferative activity against many types of cancer cells. (22)
• Cardiotonic / Cycloeucalenol and Cycloeucalenone: Study isolated two triterpenes from the stems, namely, cycloeucalenol and cycloeucalenone. Results showed mild cardiotonic effects: cycloeucalenol slightly increased right atrial force contractions and reduction in left atria of rat in vitro, while cycloeucalenone showed slight change from control on right and left atrial force. (23)
A research conducted in the Indian Medicine Research Laboratory in Sri Ramachandra University, studied the mechanism of the active ingredients of Tinospora cordifolia against key marker cells of insulin dependent glucose transporter-4 (Glut-4) and the predominant protein that influences glucose metabolism. According to results, the Glut-4 and the dominant protein were modulated by Tinospora cordifolia, Moreover, the uptake of glucose was likewise mediated suggesting the anti-diabetic properties of TC compounds. (Phytomedicine Feb 2013: Anti-diabetic Property of Tinospora Cordifolia)
Anti-Radiation Properties of Tinospora Cordifolia
In a clinical report from the Radiation and Cancer Biology Laboratory of the University of Rajasthan, India, the anti-radiation property of Tinospora cordifolia has been positively identified. In the study of a group of male mice that was subjected to gamma radiation, results have shown that those pre-treated with Tinospora cordifolia extracts exhibited less testicular lesions as compared to a control group. This suggests the radiation protective activity of Tinospora cordifolia in testicular radiation induced lesions. (eCAM 2011: Radiation-induced Testicular Injury and its Amelioration by Tinospora Cordifolia Extract)
Anti-Cancer Properties of Tinospora cordifolia
The Division of Ethnopharmacology of Loyola College in India conducted a study on the effects of Tinospora cordifolia extracts against induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in rats to determine its potential use in cancer therapy. Results have shown that those treated with Tinospora cordifolia extracts (TCE) exhibited an increased level of antioxidants and detoxification enzymes, and decreased serum transaminase level and hepatic marker enzymes to near normal. TCE likewise reduced tumor incidence and reversed the damaged hepatocytes to normal. The study concludes that TCE exhibits preventive effect against chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats and further suggests that Tinospora cordifolia extract can be a potent chemopreventive drug for HCC. (Investigational New Drugs, August 2011: Chemopreventive potential of Epoxy clerodane diterpene from Tinospora cordifolia against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma)
Tinospora cordifolia activity against Allergy
The efficacy of Tinospora cordifolia (TC) extract in patients of allergic rhinitis was assessed in a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial in the Department of Pharmacology, Indira Gandhi Medical College, India. Results have shown that those treated with Tinospora cordifolia extracts exhibited less symptoms as against those who were not. The statistical results indicated a significant difference that confirms the effectiveness of Tinospora cordifolia against allergic rhinitis. (Journal of Ethnopharmacology. January 2005: Efficacy of Tinospora cordifolia in allergic rhinitis)
Effects of Tinospora cordifolia to Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
The Division of Endocrinology, University of Göttingen in Germany conducted a laboratory investigation on the effects of beta-Ecdysone (ECD), a steroid found in Tinospora cordifolia extract on joints, epiphyseal cartilage and trabecular tissues in rats. The study has shown that rats subjected to treatment of ECD have developed thicker joint cartilage and thicker epiphyseal growth plate. The study suggests that Tinospora cordifolia has antiosteoporotic effects and may be of value in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis which is of increasing importance due to aging and obesity among individuals. (Phytomedicine, April 2010: Beneficial effects of beta-Ecdysone on the joint, epiphyseal cartilage tissue and trabecular bone in ovariectomized rats)

• Hay Fever / Allergic Rhinitis: A study in the Indira Ghandi Medical College showed it effective in relieving symptoms of hay fever or allergic rhinitis. The study used the supplement Tinofend 300 mg three times a day.
• Anti-scabies: Tinospora rumphii Boerl. (Makabuhay) in the Treatment of Scabies: The study established the acaricidal property of Tinospora rumphii. A concomitant antimicrobial action could not be ruled out.
• Furanoid Diterpenes: Study yielded cleordane type furanoid diterpenes: a new rumphioside I and known borapetodies C and F, plus three other compounds. (6)
• Clerodane Diterpenes: Study yielded two new diterpenes, 1 and 2, from the leaves of Tinospora rumphii, along with known compounds tinotufolin D and vitexilactone. (7)
• Swine Diarrhea Control: Study showed reduction of diarrhea with use of 25% fresh makabuhay decoction from day 15-35 in piglets with diarrhea. (8)
• Antifertility Effect: Study on Sprague-Dawley rats investigated the effect of T rumphii on the activity of 3-B-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in the ovary. (9)
• Hypoglycemic / Hypolipidemic: Study on the extract of Tinospora cordifolia roots for 6 weeks resulted in a significant reduction of blood and urine glucose and lipids in serum and tissues in alloxan diabetic rats.
(10)
• Antimicrobial / Diterpenes: Study on chloroform extract of air-dried leaves yielded a new clerodane diterpene, B2, and known diterpenes B1, tinotufolin D (B5) and vitexilactone (B3). B2 was found to have antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger and T. mentagrophytes, and antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis. (11)
• Hypoglycemic / Insulinotropic Activity: Study of aqueous extract on alloxan-diabetic rats showed significant reduction of blood glucose and higher levels of serum insulin levels. The insulinotropic effect was also evident in perifused human and rat islets and HIT-T5 B cells. Results suggest the hypoglycemic effect is associated with increased insulin secretion. (14)
• No Diabetic Benefits / Human Study: Study of dry powder capsule of Tinospora crispa in healthy and type 2 diabetic patients showed no effect on serum glucose and insulin levels. The result was inconsistent with other studies in animal model and metabolic syndrome subjects. (15)
• Anti-TNF-a / Prevention of Atherosclerosis-related Cardiovascular Diseases: Study investigated an aqueous and methanol extract on Tumor Necrosis Factor induced inflammation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial cells in vitro. Results showed T. crispa extracts have an inhibitory effect in vitro on the levels of inflammation signaling molecules and may have potential in the development of nutraceuticals for the prevention of atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular diseases. (16)
• Toxicity Study / Prolonged Use Concern: Results of chronic toxicity study of ethanolic extract suggest that, due to observed hepatic and renal toxicity potential in rats, prolonged use of high doses of T. crispa in humans should be avoided or discontinued immediately if signs of liver or renal toxicities occur while using T. crispa. (17)
• Antimicrobial / Cytotoxicity / Antioxidant: Various extracts showed very significant cytotoxicity on brine shrimp lethality bioassay. Strong antioxidant activity was seen on DPPH assay. A chloroform soluble fraction of the methanolic extract showed significant activity against tested organisms on antimicrobial screening. (18)
• Borapetoside C / Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Study isolated the hypoglycemic actions of borapetoside C isolated from T. crispa. Results showed borapetoside C can increase glucose utilization, delay the development of insulin resistance and enhance insulin sensitivity. (19)
• Antioxidative / Antiatheroslcerosis: Study investigated the effect of T. crispa stem aqueous extract in hypercholesterolemic-induced rabbits. Results showed improvement in lipid profile (decreased total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL, and increased HDL). Extract also showed strong antioxidative properties and markedly reduced atheroslcerotic lesion formation. Results suggest a potential for incorporation of T. crispa as part of therapeutic regimens in the prevention of atherosclerosis. (20)
• Hepatotoxin Concerns: Study evaluated the effect of an ethanolic extract of dried stems of T. crispa i a male rat model of hepatic fibrosis caused by the hepatotoxin, thioacetamide. Results showed a significant increase in the activity of liver enzymes. The in vivo study establishes the extract contains hepatotoxins and suggests reliance on data from in vitro methodologies may lead to erroneous conclusions. (21)
• Antioxidative / Antiproliferative: Study evaluated the cytotoxicity potential and antioxidant activity of various extracts. A methanol extract showed the highest flavonoid and phenolic content, with highest scavenging activity in a dose-dependent manner. T. crispa also showed dose-dependent antiproliferative activity against many types of cancer cells. (22)
• Cardiotonic / Cycloeucalenol and Cycloeucalenone: Study isolated two triterpenes from the stems, namely, cycloeucalenol and cycloeucalenone. Results showed mild cardiotonic effects: cycloeucalenol slightly increased right atrial force contractions and reduction in left atria of rat in vitro, while cycloeucalenone showed slight change from control on right and left atrial force. (23)


Anybody knows where i can get the plant.? Salamat
ReplyDelete